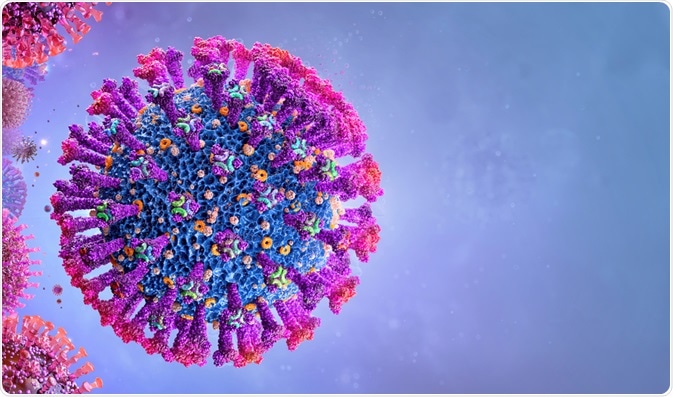
Virusに感染すると遺伝子の一部が変異する事も在ります。
Virus自体も免疫を逃れるために遺伝子を変異させて行きます。
遺伝子の塩基がアデニン(A)がグアニン(G)に変化する等の変化が起きるんです。
此れは、RNAvirusは、変異が早い理由は、遺伝子の塩基が変異し易いだけじゃ無くてRNAの塩基結合が安定していないために別種の同属VirusのRNAとも結合するためです。
DNAvirusは、変異し難いですが此れは、DNAが同じ塩基結合をし様とする事で変異が少ない。
此れでVirusが動物や植物に感染すると宿主の遺伝子の塩基を入れ換えて仕舞い突然変異の原因と成ります。
RNAvirusで宿主遺伝子変異ですがVirusのRNAがDNAをエピゲノム通じて騙してDNAを複製するmRNAに宿主の遺伝子と別情報を与えています。
宿主の遺伝子と別情報を与えるためにVirusのRNAが細胞内に残存して代々受け継がれます。
DNAvirusが宿主の遺伝子変異の原因と成るのは、VirusのDNAが宿主のDNAと入れ替わるやVirusのDNAが細胞内全身の細胞内に残存して宿主の遺伝子変異の原因と成ります。
Viruses as environmental mutagenic factors - PubMed
Injections into Drosophila melanogaster males of 9 DNA- and RNA-containing viruses non-infectious for this insect, proved that all of them are highly mutagenic, ...
PubMed
What is a Viral Mutation?
This article looks at what we mean when we refer to a viral mutation.
News-Medical
How Do Viruses Mutate, and What Is the Role of Epidemiology?
Why are diseases like COVID-19 so hard to treat, and how do viruses mutate? Learn why viruses mutate and how COVID-19 epidemiology has advanced public health.
School of Public Health
How Do Viruses Mutate and What it Means for a Vaccine? | Pfizer