純粋な水には電流が流れないし、固形の塩化ナトリウムには電流は流れないのに、これらを混合して水溶液にすると電流が流れるようになる。
同様に、うすい塩酸やうすい水酸化ナトリウム水溶液、塩化銅水溶液にも電流が流れる。
一方で、エタノール水溶液には電流は流れない。
水に溶けたとき電流が流れるようになる物質を電解質、水に溶けても電流が流れない物質を非電解質という。
Pure(distilled) water cannot conduct electric current.
Also solid Sodium chloride cannot conduct current.
But when they are mixed and become solution, they can conduct current.
In the same way, dilute Hydrochroric acid, dilute Sodium hydroxide solution and Copper chroride solution can conduct current.
On the other side, ethanol solution cannot conduct current.
"Electrolytes" can conduct current when they dissolve in water, but "non-electrolytes" cannot conduct current even when they dissolve in water.
電解質の水溶液に電流を流すと、電極付近に泡が出るなど変化が見られた。
特に塩化銅水溶液に電流を流すと、陰極には赤い物質が付着し、陽極付近には気体が発生する。
赤い物質はこすると金属光沢を呈し、電流を通す。
この結果から、陰極に付着した物質は銅であることがわかる。
一方、気体の性質を調べると、プールのような刺激臭がし、赤インクの色を脱色する。
この結果から、陽極に発生した気体は塩素であることがわかる。
これらのことから塩化銅水溶液に電流を流すと、電気分解が起こって銅Cuと塩素Cl2が発生することがわかる。
この化学変化を化学反応式で表すと、
塩化銅 → 銅 + 塩素
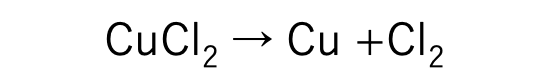
塩化銅水溶液と同様に硫酸銅水溶液や硝酸銅水溶液に電流を流すと、いずれも陰極に銅が付着する。
一方、塩化鉄水溶液に電流を流すと、陰極には鉄が付着し、陽極には塩素が発生する。
これらのことから電解質の水溶液に電流を流したとき、生じる物質は決まった側の電極から現れることがわかる。
When you flow electric current into solutions of electrolyte, you can see bubbles or other change on both electrodes.
Especially, when you flow current into Copper chroride solution, you can see red material on negative electrode and bubbles near positive electrode.
If you rub the red material you can see metallic luster and it can conduct current so that you can realize it is Copper.
On the other side, gas of bubbles smells like pool and bleachs red ink so that you can realize the gas is Chlorine.
According to these results of experient, when you flow current through Copper chloride you can know that electrolysis occurs and Copper(Cu) and Chlorine(Cl2) appear.
I show you this chemical change as formula below,
Copper chloride → Copper + Chlorine
As a same way of Copper chloride solution when you flow current through Copper sulfate or Copper nitrate solution you can see Copper on negative electrode either.
Also when you flow current through Iron chloride, you can see Iron on negative electrode and chlorine near positive electrode.
From these results, you can know that produced substances appear on specific electrode when you flow current into electrolyte solution.
原子は中心に+の電気を持つ原子核があり、そのまわりにーの電気を持つ電子がある。
原子核は+の電気を持つ陽子(ようし)と電気を持たない中性子からできている。
原子核と電子はお互いの電気を打ち消し合うので、原子は全体としては電気を持たない。
原子核に含まれる陽子の数は原子の種類によって決まっている。
また、普段原子に含まれる陽子の数と電子の数は同じである。
原子の種類は同じであっても、原子核に含まれる中性子の数が違うものを互いに同位体と呼ぶ。
An atom has positive charged nucleus at its center and has some negative charged electrons around a nucleus.
A nucleus has some positive charged protons and some non-charged neutrons.
The nucleus and electrons cancel each other's electric charge, so the atom as a whole has no charge.
The number of protons in the nucleus depends on the kind of atom(element).
Normally, the number of protons in the nucleus(atom) is equal to the number of electrons in the atom.
If the kind of atoms are same but they have different number of neutrons, they are called isotopes of each other.

原子は通常電気を帯びていないが、電子を失ったり得たりすることで電気を帯びるようになり、これをイオンという。
電子を失って+の電気を帯びたイオンを陽イオン、電子を得てーの電気を帯びたイオンを陰イオンという。
Usually, atoms are not charged electrically but they are charged when they lose or gain electrons and they are called ions.
The ions which lose electrons are called + ion (cation) and they are positive charged, on the other hand the ions which gain electrons are called - ion (anion) and they are negative charged.
電解質の固体は陽イオンと陰イオンがお互いに引き合って結びついてできている。
電解質が水に溶けて、陽イオンと陰イオンに分かれることを電離という。
非電解質は水に溶けても電離しないので、電流が流れない。
塩化銅と塩化ナトリウムの電離を化学式を使って表すと下のようになる。
Electrolyte solids are made up of + ion and - ion that attract and bond with each other.
When an electrolyte dissolves in water and separates into + ion and - ion, that is called ionization.
Non-electrolytes do not ionize when it dissolve in water so that electric current cannot flow through them.
The ionization of Copper chloride and Sodium chloride is shown as formula below.