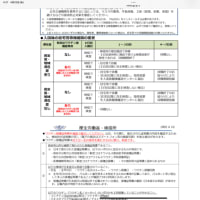
世界のメジャー航空会社の業界団体「国際航空運送協会」通称IATA(イアタ、アイアタ)(International Air Transport Association)、今ではその存在価値は薄弱化されて、旦那衆の寄り合い場所と化したとの認識ですが、その団体が以下のレポートを出していますが、
そこから読み解ける事は2点、猿でもすぐに解るのが、
・古い機材での事故
・燃費効率が悪い古い機材での航空運賃高騰
2024年新規機体納入数は1,254機
2018年1,813機から大幅に減少
2025年新規1,802機の納入が予想
従来予測2,293機には届かず
世界で運用している旅客機35,166機(ロシア機も含)14%の5000機がハンガー入りしている(以下の本文では“parked“としていますが、小生なら“hanger“ と書きたい
*ハンガー(hangar)は、 航空機を保管する目的の他に、整備や点検、修理、洗浄等をするために使われる専門用語
世界で運用している旅客機35,166機の2%の700機がエンジン点検と
Supply Chain Issues Continue to Negatively Impact Airline Performance into 2025
The International Air Transport Association (IATA) expects severe supply chain issues to continue to impact airline performance into 2025, raising costs and limiting growth.
IATA quantified the scale of the challenges facing airlines because of supply chain issues in its latest airline industry outlook:
- Average age of the global fleet has risen to a record 14.8 years, a significant increase from the 13.6 years average for the period 1990-2024.
- Aircraft deliveries have fallen sharply from the peak of 1,813 aircraft in 2018. The estimate for 2024 deliveries is 1,254 aircraft, a 30% shortfall on what was predicted going into the year. In 2025, deliveries are forecast to rise to 1,802, well below earlier expectation for 2,293 deliveries with further downward revisions in 2025 widely seen as quite possible.
- The backlog (cumulative number of unfulfilled orders) for new aircraft has reached 17,000 planes, a record high. At present delivery rates, this would take 14 years to fulfil, double the six-year average backlog for the 2013-2019 period. However, the waiting time is expected to shorten as delivery rates increase.
- The number of “parked” aircraft is 14% (approximately 5,000 aircraft) of the total fleet (35,166 as at December 2024, including Russian-built aircraft). While this has improved recently, parked aircraft remain 4 percentage points higher than pre-pandemic levels (equivalent to some 1,600 aircraft). Of these, 700 (2% of the global fleet) are parked for engine inspections. We expect this situation to persist into 2025.
“Supply chain issues are frustrating every airline with a triple whammy on revenues, costs, and environmental performance. Load factors are at record highs and there is no doubt that if we had more aircraft they could be profitably deployed, so our revenues are being compromised. Meanwhile, the aging fleet that airlines are using has higher maintenance costs, burns more fuel, and takes more capital to keep it flying. And, on top of this, leasing rates have risen more than interest rates as competition among airlines intensified the scramble to find every way possible to expand capacity. This is a time when airlines need to be fixing their battered post-pandemic balance sheets, but progress is effectively capped by supply chain issues that manufacturers need to resolve,” said Willie Walsh, IATA’s Director General.
Specifically, IATA noted that, persistent supply chain issues at least partially responsible for two negative developments:
- Fuel efficiency (excluding the impact of load factors) was unchanged between 2023 and 2024 at 0.23 litres/100 available tonne kilometers (ATK). This is a step back from the long-term (1990-2019) trend of annual fuel efficiency improvements in the range of 1.5-2.0%.
- Exceptional demand for leased aircraft pushed leasing rates for narrow body aircraft to levels 20-30% higher than in 2019.
“The entire aviation sector is united in its commitment to achieving net zero carbon emissions by 2050. But when it comes to the practicality of actually getting there, airlines are left bearing the biggest burden. The supply chain issues are a case in point. Manufacturers are letting down their airline customers and that is having a direct impact of slowing down airlines’ efforts to limit their carbon emissions. If the aircraft and engine manufacturers could sort out their issues and keep their promises, we’d have a more fuel-efficient fleet in the air,” said Walsh.
> Read the Global Outlook for Air Transport




















※コメント投稿者のブログIDはブログ作成者のみに通知されます