import pandas as pd
import zipfile
import string
import re
import os
def parse(fn, encoding='latin1', df_name='df', abbreviate=True, minlength=10, verbose=False):
"""
fn: *.zip ファイル(入力) unzip されアスキーデータ *.dat ができる
*.dat があれば,それを使う
この関数は,return() でデータフレームを返すので,すぐ分析を開始できる
副次効果として,df.read_csv() で読める *.csv ファイルを書く
変数情報をデータフレーム *-info.csv に書く
さらに,カテゴリーデータ値を数値ではなく文字列に変換したデータファイルとして読む *-templeta.py ファイルを書く
このテンプレートを使って分析プログラムを書けばよい
abbreviate = True のとき,カテゴリー変数のカテゴリー名を minlength の長さで短縮する
"""
def parse2(arg, f, t):
pos = [i for i, s in enumerate(variable) if arg[0] in s][0]
f[pos] = int(arg[1])
t[pos] = int(arg[3])
def is_num(a):
return all(s in '.0123456789' for s in str(a))
base = fn.replace('.zip', '')
if not os.path.exists(base + '.dat'):
with zipfile.ZipFile(fn) as zip_file:
zip_file.extractall()
fn = str.upper(base) + '.sps'
f = open(fn, encoding=encoding)
src = f.read().split('\n')
f.close()
src = [s.strip() for s in src]
# 最大読み取り桁
s = [s for s in src if 'LRECL' in s]
lrecl = int(re.sub('/LRECL=', '', s[0]))
# df に,変数名と変数ラベルを取り出す
variable = []
label = []
i = [i for i, s in enumerate(src) if s.startswith('VARIABLE LABELS')][0] + 1
while src[i] != '.':
s = src[i].split('"')
variable.append(s[0].replace(' ', ''))
label.append(s[1])
i += 1
n_variables = len(variable)
# df に,読み出し桁数の情報を追加する
f = [0] * n_variables
t = [0] * n_variables
i = [i for i, s in enumerate(src) if s.startswith('DATA LIST FILE')][0] + 1
while src[i] != '.':
field = src[i].replace('(A)', '').split()
if len(field) == 4:
parse2(field, f, t)
elif len(field) == 8:
parse2(field[:4], f, t)
parse2(field[4:], f, t)
else:
print('parse error_')
return 999
i += 1
w = [j - i + 1 for i, j in zip(f, t)]
colspecs = [(i - 1, j) for i, j in zip(f, t)]
df = pd.DataFrame({'variable': variable, 'label': label, 'from': f, 'to': t, 'width': w})
# *.sps の変数に関するデータフレームの書き出し
df.to_csv(base + '-info.csv', index=False)
# データフレームとして読み込み
if sum(w) != lrecl:
print(f'widths error. sum of widths = {sum(w)}, lrecl = {lrecl}\n')
return 999
fn5 = base + '.dat'
print(f'read {fn5} ...')
df2 = pd.read_fwf(fn5, colspecs=colspecs, header=None)
df2.columns = variable
n = df2.shape[0]
print(f' {n} cases, {n_variables} variables')
# csv ファイル書き出し
df2.to_csv(base + '.csv', index=False)
###
# もっとも単純にデータをインポートするだけなら,以下は要らない。
i = [i for i, s in enumerate(src) if s.startswith('VALUE LABELS')][0] + 1
f = open(base + '-template.py', mode='w')
f.write('import pandas as pd\n')
f.write('%s = pd.read_csv("%s.csv")\n' % (df_name, base))
old_str = []
new_str = []
variable = src[i]
i += 1
while True:
if len(src[i]) == 0 or src[i][0] == '/':
if verbose:
print(f'decoding ... {variable}')
if abbreviate:
new_str = [str(s) + ':' + t[:minlength+1] for s, t in zip(old_str, new_str)]
x = df2.loc[:, variable].dropna()
category = [int(y) if is_num(y) else y for y in sorted(set(x))]
count = 0
for s in category:
if not s in old_str:
old_str.insert(count, s)
new_str.insert(count, str(s))
count += 1
if verbose and count != 0:
print(f'levels are completed.')
print(new_str)
dic = {}
dic_str = '{'
for key, value in zip(old_str, new_str):
dic.setdefault(key, value)
if is_num(key):
dic_str = dic_str + str(key) + ': "' + value + '", '
else:
dic_str = dic_str + '"' + key + '": "' + value + '", '
df2 = df2.replace({variable: dic})
dic_str = re.sub(', $', '}', dic_str)
f.write("%s = %s.replace({'%s': %s})\n" % (df_name, df_name, variable, dic_str))
if len(src[i]) == 0:
break
old_str = []
new_str = []
variable = src[i].split()[1]
else:
field = src[i].split('"')
if len(field) == 3:
old_str.append(int(field[0].strip()))
new_str.append(field[1])
elif len(field) == 5:
old_str.append(int(field[1]) if is_num(field[1]) else field[1])
new_str.append(field[3])
i += 1
f.close()
return df2
value labels に記述されない値が NA になってしまう件を修正
parse = function(fn, df.name = "df", abbreviate = TRUE, minlength = 10, verbose = FALSE) {
# fn: *.zip ファイル(入力) unzip されアスキーデータ *.dat ができる
# invisible() でデータフレームを返す
# *.csv ファイルを書く
# 変数情報についてのデータフレーム *-info.csv に書く
# R でfactor 変数を定義するための R コードを *-template.R に書く
# abbreviate = TRUE のとき,factor() の labels を minlength の長さで短縮する
parse2 = function(df, arg) {
pos = grep(arg[1], df$variable)
df[pos, "from"] = as.integer(arg[2])
df[pos, "to"] = as.integer(arg[4])
return(df)
}
base = sub("\\..*$", "", fn)
if (grepl('\\.zip$', fn) && ! file.exists(paste0(fn, ".dat"))) {
unzip(fn)
}
fn = paste0(toupper(base), ".sps")
src = readLines(fn, encoding="latin1")
src = trimws(src)
pos = grep("LRECL", src)
# 最大読み取り桁
lrecl = as.integer(unlist(strsplit(src[pos], "="))[2])
# df に,変数名と変数ラベルを取り出す
begin = which(src == "VARIABLE LABELS")
n.variable = which(src[-(1:begin)] == ".") - 1
variable = character(n.variable)
label = character(n.variable)
for (i in 1:n.variable) {
field = unlist(strsplit(src[begin + i], '"'))
variable[i] = trimws(field[1])
label[i] = field[2]
}
n.variables = length(variable)
# df に,読み出し桁数の情報を追加する
df = data.frame(variable, label, from=0, to=0, width=0)
begin = which(grepl("DATA LIST FILE", src))
n.def = which(src[-(1:begin)] == ".") - 1
for (i in 1:n.def[1]) {
s = gsub("\\(A\\)", "", src[begin + i])
field = unlist(strsplit(s, " +"))
pos = which(field %in% df$variable)
if (length(pos) == 1) {
df = parse2(df, field)
} else if (length(pos) == 2) {
df = parse2(df, field[1:4])
df = parse2(df, field[5:8])
} else {
print("parse error.")
return(999)
}
}
df$width = df$to - df$from + 1
# *.sps の変数に関するデータフレームの書き出し
write.csv(df, paste0(base, "-info.csv"), row.names = FALSE)
# データフレームとして読み込み
if (sum(df$width) != lrecl) {
cat("widths error. sum of widths =", sum(df$width), ", lrecl =", lrecl, "\n")
return(999)
}
fn5 = paste0(base, ".dat")
cat(sprintf("read %s...\n", fn5))
df2 = read.fwf(fn5, width = df$width)
colnames(df2) = df$variable
n = nrow(df2)
cat(sprintf(" %d cases, %d variables\n", n, n.variables))
# csv ファイル書き出し
fn6 = paste0(base, ".csv")
write.csv(df2, fn6, row.names = FALSE)
###
# もっとも単純にデータをインポートするだけなら,以下は要らない。
i = which(src == "VALUE LABELS") + 1
fn7 = paste0(base, "-template.R")
write(sprintf("# template file for data frame -- %s.csv", base), fn7)
write(sprintf("%s = read.csv('%s.csv')", df.name, base), fn7)
old.str = new.str = NULL
variable = src[i]
while (TRUE) {
if (nchar(src[i]) == 0 || substr(src[i], 1, 1) == "/") {
if (verbose) {
cat("decoding...", variable, "\n")
}
if (abbreviate) {
new.str = base::abbreviate(new.str, minlength = minlength, named = FALSE)
new.str = paste(old.str, new.str, sep=":")
}
# もともと存在する level なのに,levels で指定漏れになると存在しないことになるのを修正
category = sort(unique(df2[, variable]))
count = 0
for (s in category) {
if (nchar(trimws(s)) != 0 && ! s %in% old.str) {
old.str = append(old.str, s, after=count)
new.str = append(new.str, s, after=count)
count = count + 1
}
}
df2[, variable] = factor(df2[, variable], levels = old.str, labels = new.str)
old.str2 = sapply(old.str, function(s)
if (is.numeric(s)) s else paste0("'", s, "'"))
old.str2 = paste(old.str2, collapse = ", ")
new.str2 = paste(sprintf("\"%s\"", new.str), sep = ", ", collapse = ", ")
cat(sprintf('%s$%s = factor(%s$%s, levels=c(%s), labels=c(%s))\n',
df.name, variable, df.name, variable, old.str2, new.str2 ),
file = fn7, append = TRUE)
if (nchar(src[i]) == 0) {
break
}
old.str = new.str = NULL
variable = unlist(strsplit(src[i], " "))[2]
} else if (nchar(src[i]) != 0) {
field = unlist(strsplit(src[i], "\\\""))
n.field = length(field)
if (n.field == 2) {
old.str = c(old.str, as.integer(field[1]))
new.str = c(new.str, field[2])
} else if (n.field == 4) {
old.str = c(old.str, field[2])
new.str = c(new.str, field[4])
}
}
i = i + 1
}
invisible(df2)
}
最新版は以下を参照
"2014 NHPI NHIS Data" を R にインポート Ver. 3
https://blog.goo.ne.jp/r-de-r/e/23dae09d759881be24d0bb2a645ce8ac
"2014 NHPI NHIS Data" を Python にインポート Ver. 1
https://blog.goo.ne.jp/r-de-r/e/c25c3b84e3e1e50136958939501380b0
factor() の labels を base::abbreviate() で短縮するオプションを付加
parse = function(fn, df.name = "df", abbreviate = TRUE, minlength = 10, verbose = FALSE) {
# fn: *.zip ファイル(入力) unzip されアスキーデータ *.dat ができる
# invisible() でデータフレームを返す
# *.csv ファイルを書く
# 変数情報についてのデータフレーム *-info.csv に書く
# R でfactor 変数を定義するための R コードを *-factor.R に書く
# abbreviate = TRUE のとき,factor() の labels を minlength の長さで短縮する
parse2 = function(df, arg) {
pos = grep(arg[1], df$variable)
df[pos, "from"] = as.integer(arg[2])
df[pos, "to"] = as.integer(arg[4])
type = ""
if (length(arg) == 5) {
type = arg[5]
}
df[pos, "type"] = type
return(df)
}
base = sub("\\.dat", "", sub("./", "", unzip(fn)))
fn = paste0(toupper(base), ".sps")
src = readLines(fn)
src = sub("^ +", "", src)
src = sub("\xfc\xbe\x8d\x93\xa0\xbc", " ", src) # "Ö" SAMADULT.sps などに特有
src = sub("\xfc\xbe\x8c\xa3\xa4\xbc", "'", src) # "í" SAMADULT.sps などに特有
pos = grep("LRECL", src)
# 最大読み取り桁
lrecl = as.integer(unlist(strsplit(src[pos], "="))[2])
# df に,変数名と変数ラベルを取り出す
begin = which(src == "VARIABLE LABELS") + 1
end = which(src == "VALUE LABELS") - 3
n.variables = end - begin + 1
variable = character(n.variables)
label = character(n.variables)
for (i in begin:end) {
j = i - begin + 1
variable[j] = sub(" +", "", substr(src[i], 1, 8))
label [j] = sub("\\\"", "", substr(src[i], 12, nchar(src[i])))
}
# df に,読み出し桁数の情報を追加する
df = data.frame(variable, label, from=0, to=0, width=0, type="")
begin = which(grepl("DATA LIST FILE", src)) + 1
end = which(src == "VARIABLE LABELS") - 3
for (i in begin:end) {
field = unlist(strsplit(src[i], " +"))
pos = which(field %in% df$variable)
if (length(pos) == 1) {
df = parse2(df, field)
} else if (length(pos) == 2) {
df = parse2(df, field[pos[1]:(pos[2] - 1)])
df = parse2(df, field[pos[2]:length(field)])
} else {
print("parse error.")
return(999)
}
}
df$width = df$to - df$from + 1
# *.sps の変数に関するデータフレームの書き出し
fn4 = paste0(base, "-info.csv")
write.csv(df, fn4, row.names = FALSE)
# データフレームとして読み込み
if (sum(df$width) != lrecl) {
cat("widths error. sum of widths =", sum(df$width), ", lrecl =", lrecl, "\n")
return(999)
}
fn5 = paste0(base, ".dat")
cat(sprintf("read %s...\n", fn5))
df2 = read.fwf(fn5, width = df$width)
colnames(df2) = df$variable
n = nrow(df2)
cat(sprintf(" %d cases, %d variables\n", n, n.variables))
# csv ファイル書き出し
fn6 = paste0(base, ".csv")
write.csv(df2, fn6, row.names = FALSE)
###
# もっとも単純にデータをインポートするだけなら,以下は要らない。
begin = which(src == "VALUE LABELS") + 1
end = which(src == "EXECUTE.")
fn7 = paste0(base, "-factor.R")
write("# read.csv() then source(*this file*)", fn7)
for (i in begin:end) {
if (i == begin) {
old.str = new.str = NULL
variable = src[i]
} else if (nchar(src[i]) == 0 || substr(src[i], 1, 1) == "/") {
if (verbose) {
cat("decoding...", variable, "\n")
}
if (abbreviate) {
new.str = base::abbreviate(new.str, minlength = minlength, named = FALSE)
new.str = paste(old.str, new.str, sep=":")
}
df2[, variable] = factor(df2[, variable], levels = old.str, labels = new.str)
old.str2 = paste(old.str, collapse = ", ")
new.str2 = paste(sprintf("\"%s\"", new.str), sep = ", ", collapse = ", ")
cat(sprintf('%s$%s = factor(%s$%s, levels=c(%s), labels=c(%s))\n',
df.name, variable, df.name, variable, old.str2, new.str2 ),
file = fn7, append = TRUE)
if (nchar(src[i]) == 0) {
break
}
old.str = new.str = NULL
variable = unlist(strsplit(src[i], " "))[2]
} else {
field = unlist(strsplit(src[i], "\\\""))
if (length(field) == 2) { # SAMADULT.sps などで例外
old.str = c(old.str, as.integer(field[1]))
new.str = c(new.str, field[2])
}
}
}
invisible(df2)
}
最新版は以下を参照
"2014 NHPI NHIS Data" を R にインポート Ver. 3
https://blog.goo.ne.jp/r-de-r/e/23dae09d759881be24d0bb2a645ce8ac
"2014 NHPI NHIS Data" を Python にインポート Ver. 1
https://blog.goo.ne.jp/r-de-r/e/c25c3b84e3e1e50136958939501380b0
中澤さんが https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis/nhpi/nhpi_2014_data_release.htm にあるファイルを R で使えるようにプログラムを書きたいといっていたので,書いてみた。
「ここはこうしたらよいよ」というところを教えてください。
追記 2020/07/17:編集時に大域代入記号 <<- が <= になってしまっていたのを修正
parse = function(fn, df.name = "df", verbose = FALSE) {
# fn: *.zip ファイル(入力) unzip されアスキーデータ *.dat ができる
# invisible() でデータフレームを返す
# *.csv ファイルを書く
# 変数情報についてのデータフレーム *-info.csv に書く
# R でfactor 変数を定義するための R コードを *-factor.R に書く
parse2 = function(arg) {
pos = grep(arg[1], df$variable)
df[pos, "from"] <<- as.integer(arg[2])
df[pos, "to"] <<- as.integer(arg[4])
type = ""
if (length(arg) == 5) {
type = arg[5]
}
df[pos, "type"] <<- type
}
base = sub("\\.dat", "", sub("./", "", unzip(fn)))
fn = paste0(toupper(base), ".sps")
src = readLines(fn)
src = sub("^ +", "", src)
src = sub("\xfc\xbe\x8d\x93\xa0\xbc", " ", src) # "Ö" SAMADULT.sps などに特有
src = sub("\xfc\xbe\x8c\xa3\xa4\xbc", "'", src) # "í" SAMADULT.sps などに特有
pos = grep("LRECL", src)
# 最大読み取り桁
lrecl = as.integer(unlist(strsplit(src[pos], "="))[2])
# df0 に,変数名と変数ラベルを取り出す
begin = which(src == "VARIABLE LABELS") + 1
end = which(src == "VALUE LABELS") - 3
n.variables = end - begin + 1
variable = character(n.variables)
label = character(n.variables)
for (i in begin:end) {
j = i - begin + 1
variable[j] = sub(" +", "", substr(src[i], 1, 8))
label [j] = sub("\\\"", "", substr(src[i], 12, nchar(src[i])))
}
# df に,読み出し桁数の情報を追加する
df = data.frame(variable, label, from=1, to=1, width=1, type="")
begin = which(grepl("DATA LIST FILE", src)) + 1
end = which(src == "VARIABLE LABELS") - 3
for (i in begin:end) {
field = unlist(strsplit(src[i], " +"))
pos = which(field %in% df$variable)
if (length(pos) == 1) {
parse2(field)
} else if (length(pos) == 2) {
parse2(field[pos[1]:(pos[2] - 1)])
parse2(field[pos[2]:length(field)])
} else {
print("parse error.")
return(999)
}
}
df$width = df$to - df$from + 1
# *.sps の変数に関するデータフレームの書き出し
fn4 = paste0(base, "-info.csv")
write.csv(df, fn4, row.names = FALSE)
# データフレームとして読み込み
fn5 = paste0(base, ".dat")
cat(sprintf("read %s...\n", fn5))
df2 = read.fwf(fn5, width = df$width)
colnames(df2) = df$variable
n = nrow(df2)
cat(sprintf(" %d cases, %d variables\n", n, n.variables))
# csv ファイル書き出し
fn6 = paste0(base, ".csv")
write.csv(df2, fn6, row.names = FALSE)
###
# もっとも単純にデータをインポートするだけなら,以下は要らない。
begin = which(src == "VALUE LABELS") + 1
end = which(src == "EXECUTE.")
fn7 = paste0(base, "-factor.R")
write("# read.csv() then source(*this file*)", fn7)
for (i in begin:end) {
if (i == begin) {
old.str = new.str = NULL
variable = src[i]
} else if (nchar(src[i]) == 0 || substr(src[i], 1, 1) == "/") {
if (verbose) {
cat("decoding...", variable, "\n")
}
df2[, variable] = factor(df2[, variable], levels = old.str, labels = new.str)
old.str2 = paste(old.str, collapse = ", ")
new.str2 = paste(sprintf("\"%s\"", new.str), sep = ", ", collapse = ", ")
cat(sprintf('%s[, "%s"] = factor(%s[, "%s"], levels=c(%s), labels=c(%s))\n',
df.name, variable, df.name, variable, old.str2, new.str2 ),
file = fn7, append = TRUE
)
if (nchar(src[i]) == 0) {
break
}
old.str = new.str = NULL
variable = unlist(strsplit(src[i], " "))[2]
} else {
field = unlist(strsplit(src[i], "\\\""))
if (length(field) == 2) { # SAMADULT.sps などで例外
old.str = c(old.str, as.integer(field[1]))
new.str = c(new.str, field[2])
}
}
}
invisible(df2)
}
##################
##### 使用例 #####
##################
# *.zip と,対応する *.sps をダウンロードしておく
fn = "familyxx.zip" # ASCII データ(固定書式)
# pase() は,*.sps から情報を読み取る
# カテゴリーデータは spss での順序通りの factor 変数になる
df = parse(fn, df.name = "df2")
# このあと,データフレーム a を使って分析する
# なお,parse() は元の *.dat を桁数指定で読み込み,数値データとして CSV ファイルに保存する
# *.sps による value labels を R での factor とするために,source("*-factor.R") する
# parse() の df.name は 以下の read.csv で読み込むときの左辺(データフレーム名)
df2 = read.csv("familyxx.csv")
source("familyxx-factor.R")
# このあと,データフレーム df を使って分析する
# いずれのデータフレームを使っても,結果は同じになる。
table(df$FSNAP)
table(df2$FSNAP)
# parse() R ですぐ使えるデータフレームを準備するが,毎回 *.dat を読みむので無駄かもしれない
# 一度 parse() すれば *.csv が書かれるので,
# *.csv を処理する R ファイルの前方に *-factor.R をペーストしておいてやれば,無駄が省けるかも
parse(fn, df.name = "df3") # 一回だけ
# 必要に応じ
df3 = read.csv("familyxx.csv")
source("familyxx-factor.R")
table(df3$FGAH, df3$FSNAP)
# 掲載されているファイルを全て読んでみる
familyxx = parse("familyxx.zip")
funcdisb = parse("funcdisb.zip")
paradata = parse("paradata.zip")
samadult = parse("samadult.zip")
samchild = parse("samchild.zip")
personsx = parse("personsx.zip")
injpoiep = parse("injpoiep.zip")
househld = parse("househld.zip")
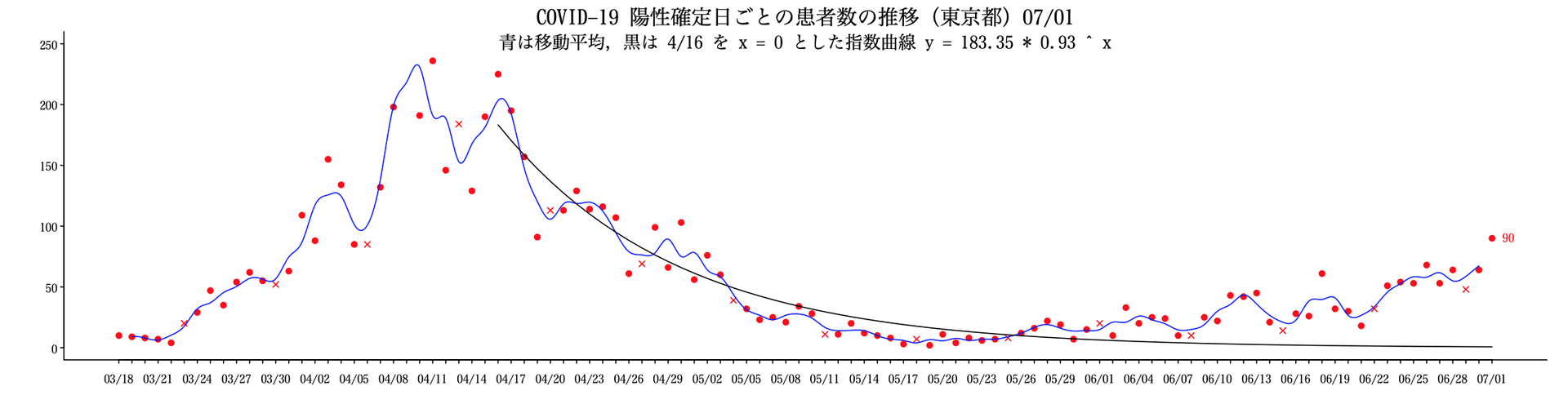
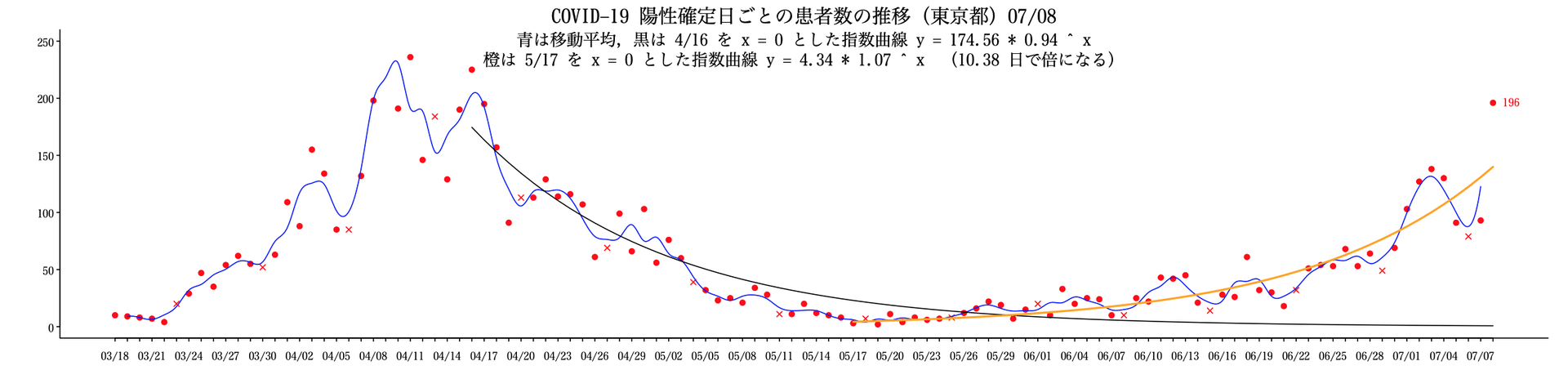
昨日の2という数字は怪しいと思っていたが案の定。
もう,誰がどう言おうと,増加の傾向は明らか。