論文情報
論文名
T-cell hyperactivation and paralysis in severe COVID-19 infection revealed by single cell analysis
著者
Bahire Kalfaoglu, José Almeida-Santos, Chanidapa Adele Tye, Yorifumi Satou, Masahiro Ono
掲載誌
Frontiers in Immunology
doi
10.3389/fimmu.2020.589380
URL
背景
新型コロナウイルス感染症は現在も拡大が続いており、我々の日常生活、社会・経済活動に甚大な影響を及ぼしています。感染者の大部分は無症状やごく軽症であるのに、なぜ一部が重症化するかは未解明の大きな疑問です。これまで指摘されている重症化のリスク因子には高齢・糖尿病・肥満・高血圧などがあります。また、重症患者では、血液中の炎症性物質(炎症性サイトカイン)の量が増え免疫系が過剰反応していることが知られる一方で、免疫細胞の司令塔「T細胞」が血液中で著しく減少していることが認められています。しかしながら、これらの知見についての医学的意味はまだ不明です。
研究の内容
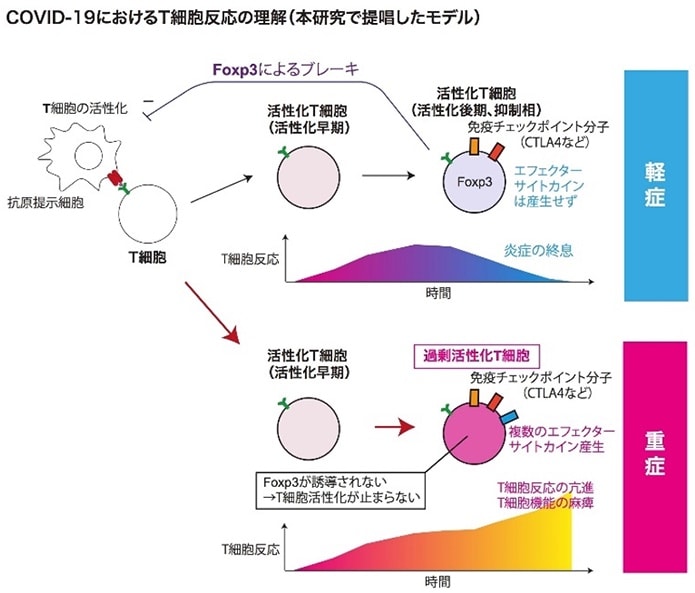
T細胞は、ウイルスを特異的に認識することで免疫系の活性を調整・指揮する細胞です。本研究では、このT細胞に注目して、肺炎重症化の原因について研究を行いました。T細胞は、新型コロナウイルス感染症においても、ウイルス排除ならびに免疫獲得に重要な役割を果たしています。中でもCD4+ T細胞(ヘルパーT細胞)は、ウイルスを攻撃する「細胞傷害性T細胞」や抗体を産生する「B細胞」の成熟・活性化を促進し、ウイルスを体内から排除する重要な働きをしています。その一方で、一部のCD4+ T細胞は高度に活性化すると転写因子*FoxP3を発現して、いわゆる抑制性T細胞(制御性T細胞)となり、T細胞反応を抑制するブレーキ役として働きます。今回の研究では、中国武漢の新型コロナウイルス感染症患者の肺組織の遺伝子データを使用して、その中に存在するCD4+ T細胞の活性ならびに遺伝子の特徴を調べました。
成果
本研究において、最先端のバイオインフォマティクス解析技術を用いて、重症化肺炎患者の肺組織ではT細胞が著明な活性化を示している一方で、FoxP3の誘導が阻害されており、T細胞の反応を止めるブレーキ機能に異常があることを見出しました。すなわち、ブレーキ機能が低下することで多くのT細胞が過剰反応し、新型コロナウイルス感染症患者の肺炎が重症化している可能性が示されました。
background
The spread of the new coronavirus infection continues and has a great impact on our daily lives, social and economic activities.While the majority of those infected are asymptomatic or have very mild disease, it is an open question as to why some people become seriously ill.Risk factors that have been noted for severe disease include old age, diabetes, obesity and hypertension.In addition, it is known that the amount of inflammatory substances (inflammatory cytokines) in the blood of patients with severe disease increases and the immune system overreacts, while the number of "T cells," the command center of immune cells, is significantly reduced in the blood of patients with severe disease.However, the medical implications of these findings are still unknown.
The study
T cells regulate and direct the activity of the immune system by specifically recognizing viruses.In this study, we focused on T cells to investigate the causes of severe pneumonia, and found that T cells play an important role in viral elimination and immune acquisition in new coronavirus infections.CD4+ T cells (helper T cells), in particular, play an important role in promoting the maturation and activation of cytotoxic T cells that attack viruses and B cells that produce antibodies, and in eliminating viruses from the body.On the other hand, some CD4+ T cells, when highly activated, express the transcription factor *FoxP3 and become so-called inhibitory T cells (regulatory T cells), which act as brakes to suppress the T cell response.In this study, the researchers used genetic data from the lung tissue of patients with novel coronavirus infection in Wuhan, China, to investigate the activity and genetic characteristics of CD4+ T cells in the tissue.
Results
In this study, using state-of-the-art bioinformatics techniques, the researchers found that while T cells were markedly activated in the lung tissues of patients with severe pneumonia, FoxP3 induction was inhibited, indicating that the brake function, which stops T cells from responding, was abnormal.In other words, a large number of T cells responded excessively due to a loss of braking function, possibly resulting in severe pneumonia in patients with new coronavirus infection.
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)

























