60%以上だとツイッターで流している人がいますが、
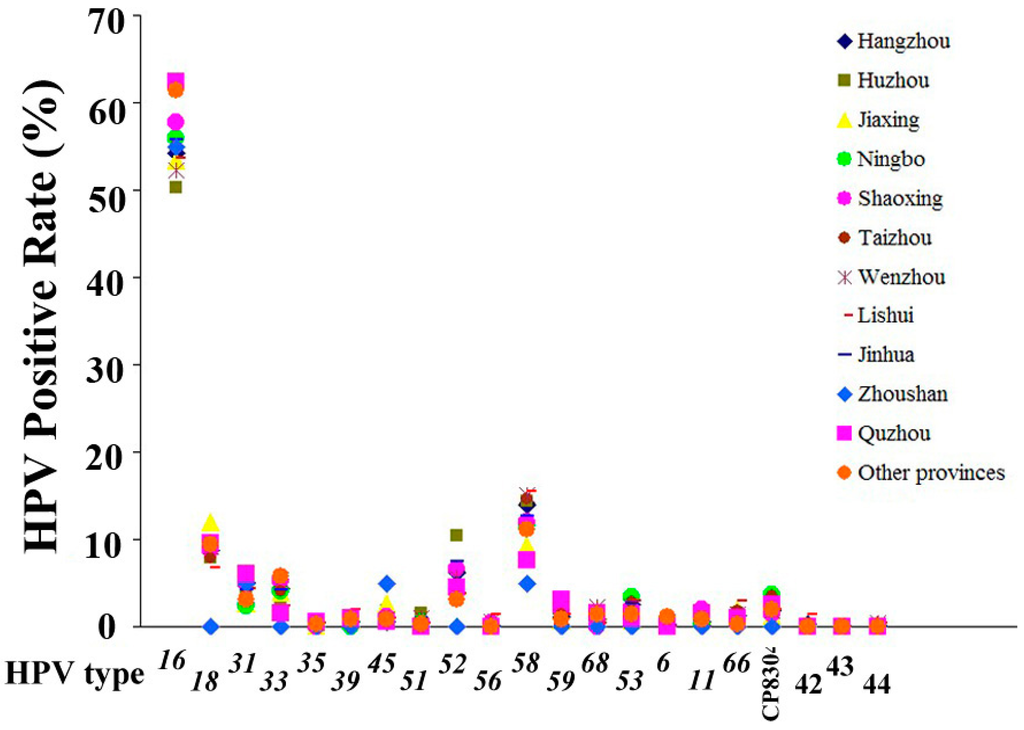
2008年の論文で、51.3%です
2008年は、Before Konno です。
2008 Jan-Feb;18(1):71-9. Epub 2007 Apr 26.
Human papillomavirus type distribution in women from Asia: a meta-analysis.
Abstract
The aim of this study was to determine human papillomavirus (HPV) type distribution in women with and without cervical neoplasia from Asia and to estimate the potential future impact of an HPV 16/18 prophylactic vaccine in this region. A meta-analysis was conducted including 79 studies using polymerase chain reaction to detect HPV types. A total of 5954, 1653, 958, and 16,803 women with invasive cervical cancer (ICC), high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL), low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL), and normal cytology or histology were included, respectively. Type-specific prevalence of HPV types 6, 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68, 70, 73, and 82 were estimated and stratified by cervical lesion grade. Overall HPV prevalence was 85.9%, 81.0%, 72.9%, and 14.4%, respectively, in women with ICC, HSIL, LSIL, and normal cytology/histology. In ICC, HPV 16 was the predominant type (52.4%), followed by HPV 18, 58, 33, 52, 45, 31, and 35. The estimated HPV 16/18-positive fraction was 66.9%, 40.4%, 26.7%, and 3.3% in women with ICC, HSIL, LSIL, and normal cytology or histology, respectively. In ICC, the estimated HPV 16/18-positive fraction was about 70% in all Asian geographic regions, with the exception of Japan (51.3%). HPV 16/18 vaccines are estimated to provide about 67% protection against ICC in Asia. HPV 58 and 52 were among the five most common types in ICC in eastern and southeastern Asia but not in south central Asia. After HPV 16 and 18, the next most six common HPV types were 58, 33, 52, 45, 31, and 35 that accounted for additional 20% of cervical cancer cases in Asia. For optimal population coverage, these HPV carcinogenic types should be considered for second-generation HPV prophylactic vaccines.












 seki_yo
seki_yo  」
」

