システムとしての求聞持法
「変身の原理」で、私は、カナダの著名な神経外科学の大家、W・ペンフィールドの発見 密教の持つすぐれた知能開発法寺聴法」のメカニズムの一端を解説した。 私はそのとき、「ひとたび修身するや、目はカメラになり、耳はテープレコーダーに変化し て、ひとたび目にし、ひとたび耳にしたことは永久に忘れなくなる技術である」と説明した。 たしかにその通りであるが、そのためにこの法を、一種の記憶力増強法、いわゆる記憶術の一 のようにうけとったひともあるようである。ページ数の関係その他の事情から十分に説明でき ず、それも無理のないことであったが、この技法が単なる記憶術のようなものであるのなら、た いした価値のないつまらないものといわればならない。なぜならば、ただ単に記憶がよくものお ぼえがよいというだけでは、ひとはよい仕事をすることができない。 ただたんにもの知りだけで はすぐれた業績をのこすことはできない。問題は、多量に持っている知識(情報)を、いかに活 用してあたらしいものを生み出すかというところにある。
い子とのよい子のちがい
ギャラップは、そるべき技術である。 知能とはなにか。 ごく大ざっぱに分けるならば、二つの
であろう。記憶と創造である。 特聡明法は、この二つのはたらきをするメカニズムに、あた らしいメカニズムをつけくわえて、あたらしい力と効果を発揮する。
この技法が、ジョージ・ギャラップや、オルダス・ハックスリーのいうように教育にとり入れ られたならば、人類のうける利益は想像することもできないほどのものである。 ギャラップのい うように、ヒトは、まさに、未来に向かって数百年の飛躍をすることができるであろう。 そういうと、そんなすばらしい技術がどうして今まで世のなかにあらわれなかったのかと、あな たは疑問に思うかも知れない。
これほどの技術が、なぜ密教寺院の片すみに埋没してしまったのか、いくつかの理由があげら れるだろうが、その最大の理由はこうである。
すぐれた古い方法がまったく見落とされてきたということは奇妙なことだ。 それに、あと になって全く忘れ去られてしまっている非常に重要な技術を発達させた個人、あるいは文化がよ くあるのだ。しかし、それらはやはり大きな価値を持ちつづけているのだ』(
といっているが、この大きな価値を持ちつづけているすぐれた方法が忘れられてしまったわけ は、それにつづくギャラップのおなじ文章のなかに見出すことができる。
システムとしての間あって、思い出される記憶と、思い出せない記憶の二つがあることを、私は、「変身の原理」 で説明した。脳の記憶のメカニズムはたいへん複雑で、それはまだ脳生理学でも十分に解明され ていないのだが、一応、その仕組みを見てみよう。
経験というのはひとつの刺激である。その刺激が記憶になるまでには、だいたいつぎのような 段階を経る刺激を感じるのは、俗にいう「五感」である。 五感とは、視覚、聴覚、味覚、嗅覚、触覚をい うが、こまかくかぞえればまだ多くの「感覚」があり、おなかが空いたとか、なんとなくけだ るく気分がよくない、とか、そういう身体の内部におこっていることを知ることもできる。つま り、われわれの身体の内部、外部におきていることがわれわれ自身にひとつの影響をおよぼす。 これが、「刺激」である。
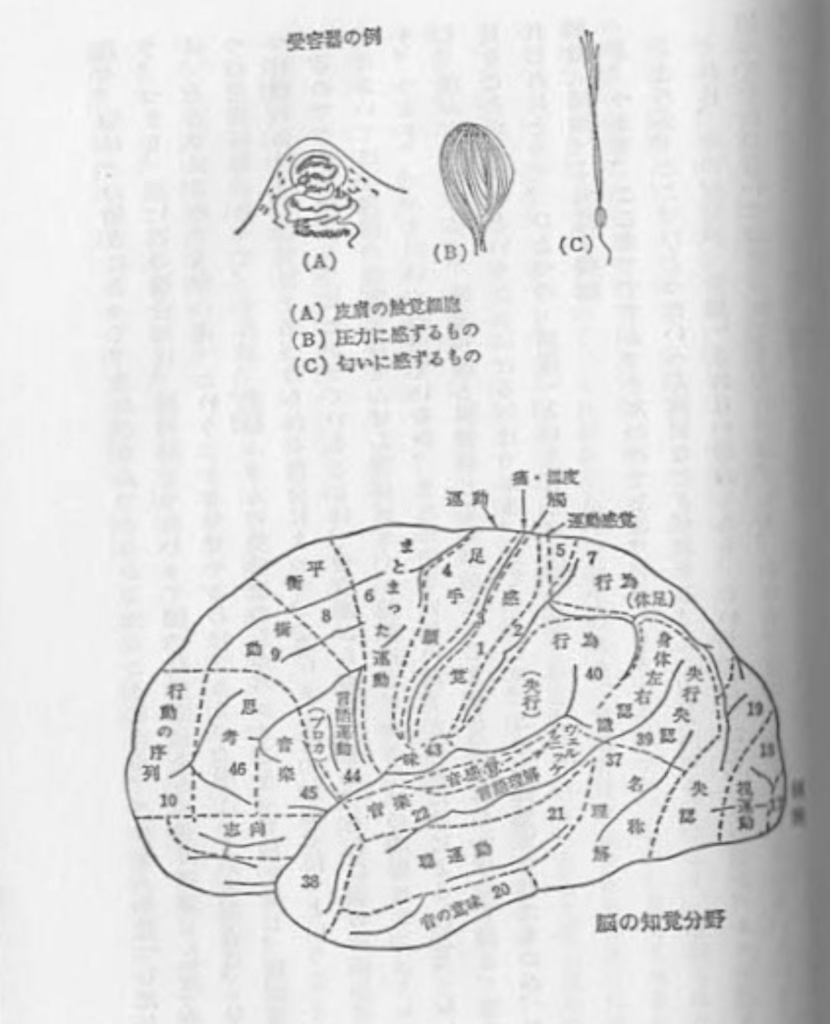
こういう刺激があると、身体にある「感覚器」または「受容器」というものがこれに反応し電気的パルスを送り出す。 たとえば、 赤い花があれば、そこから反射された光が目のレンズ を通して受容器としての視神経を刺激し、視神経がパルスを送り出す。 これはパルスであって、 刺激の強さが大きければその数がふえるだけで、電圧が大きくなるわけではない。おなじよう に、皮膚になにかが触れれば、皮膚にある受容器が圧力を感じ、その圧力に応ずる数のパルスを 神経に送りこむ 次頁の上図は、このような受容器のいくつかの例である。
さて、このようにして受容器にあたえられた
Q&A as a system
In "Principles of Metamorphosis," I described some of the mechanisms behind W. Penfield's discovery of the remarkable intellectual development of esoteric Buddhism. At that time, I explained, "Once you practice, your eyes become cameras, your ears become tape recorders, and once you see them, and once you hear them, you never forget them." This is certainly true, but for this reason, some people seem to have accepted this method as a kind of memory enhancement method, a so-called memory technique. Due to the number of pages and other factors, it was not possible to fully explain it, and it was understandable, but if this technique is just a memorization technique, it must be said that it is worthless and trivial. For one cannot do a good job simply by having a good memory and a good memory. Mere knowledge alone does not enable him to leave behind outstanding achievements. The problem lies in how to utilize the vast amount of knowledge (information) we possess to create something new.
The difference between a good child and a good child
Gallup is
Sanna
It is a technology that should be improved. What is intelligence? Roughly speaking, there are two
Will. memory and creation. In addition to the mechanisms that perform these two functions, the Tokusōmei method adds a mechanism that is unique to her, and exerts new powers and effects.
If this technique were introduced into education, as George Gallup and Aldous Huxley say, the benefits to mankind would be unimaginable. Like Gallup's man, humans could just leap hundreds of years into the future. With that said, you may wonder why such a wonderful technology has not appeared in the world until now.
There are several reasons why such a technology has been buried in a corner of Esoteric Buddhism temples, but the biggest reason is this.
It is strange that the good old method has been so overlooked. Moreover, there are many individuals, or cultures, who have developed very important skills that have since been completely forgotten. But they still have great value.”
However, the reason why this superior method of continuing great value has been forgotten can be found in the same Gallup passage that follows.
between as a system
I explained in ``The Principle of Metamorphosis'' that there are two types of memories: memories that can be recalled and memories that cannot be recalled. The mechanism of memory in the brain is extremely complex, and it has not yet been fully elucidated even in brain physiology, but let's take a look at its mechanism.
Experience is a stimulus. Before the stimulus becomes a memory, it goes through the following stages.
It is commonly known as the “five senses” to feel stimuli. The five senses are visual, auditory, gustatory, olfactory, and tactile, but there are still many more “senses” if you count them in detail, and you can also know what is happening inside your body, such as when you are hungry, or when you feel sluggish and unwell. In other words, what is happening inside and outside our bodies has an effect on us. This is the "stimulus".
When there is such a stimulus, the "sensory organs" or "receptors" in the body react to it.
Sends out electrical pulses. For example, if there is a red flower, the light reflected from it stimulates the optic nerve as a receptor through the lens of the eye, and the optic nerve sends out pulses. These are pulses, and the greater the intensity of the stimulus, the greater the number, not the greater the voltage. Similarly, when something touches the skin, the receptors in the skin feel pressure and send out a number of pulses to the nerve corresponding to that pressure.
Now, given to the receptor in this way
れる。脳はその働きによって、それがなんであるかを知ることになる。これを「知覚」したとい う。つまり、赤い花の場合には、視神経をつたわって脳の後頭葉にある視覚野に達したパルス は、そこではじめて「赤い花」ということを知覚するわけである。 「聞く」という場合は、ひと つの空気振動があって、それが、鼓膜ふきんの受容器からのパルスとなって脳に達し、側頭葉の つけ根のあたりの聴覚と名づけられる部分によって、「音」としての知覚を持つということに なるのである。現在までにわかっていることは、受容器からのパルスは、それ以後の神経伝達機 構においては受容器の種類にはぜんぜん関係がなく、純粋に、パルスだけの問題になってしま う。つまり、パルスがいくつ出ているか、または出ていないか、というだけによるので、もし も、なんらかの方法で、聴覚神経と視神経とを結びかえてしまうと、われわれは光を聞き、音を 見ることができるということになるわけである。 さて、 そこで、この「知覚」されたものが、わ れわれにとって、ひとつの「情報」ということになる。
刺激(経験)→知覚→情報
と、つまり、ここまですすんできたわけである。
こういうことになる。
ところが、ここでひとつたいへん重要なことがおきる。
それは、その知覚が「意識」されない場合もある、ということである。 受容器がパルスを送り 出してそれが届いて知覚されてもそれが必ずしも、かならず意識されるとはかぎらないという とである。「見れども見えず、聞けど いったがあん、しない。 つまり、知覚しても意識していないということである。
では、そういう意識されない信号は、情報にはならないのか?
刺激 経験ということばは、意識がともなう必要があるように思われる。つまり、意識されな 刺激は経験にならないのではないかということである。 どうであろうか。しかし考えてみると われわれは日常の行動において、 それがありふれた動作の場合、意識をはたらかせることは非常 にすくない。手なれた動作や作業の場合、ほとんど無意識でおこなっている。たとえば「道を歩 「く」というようなごくありふれた動作をする場合に、われわれはほとんど意識せずに歩くという 動作をおこなっている。いちいち足のウラの感覚器官からの情報を意識していたら、たまったも のではない。しかし、足がなにかにつまずくというような、異常な状態が起きると、間髪をいれ ず意識がはたらきだす。 ということは、それまでわれわれは異常なしという情報をうけとりつづ けていたのであるが、意識はそれに注意をはらわずにおり、異常が起きた瞬間、ただちにそちら へ意識を向け直したということであろう。
そこで考えられることは、われわれがうけとる情報は、常に一時にひとつということでなく、 いつも多数の情報が同時にかさなって入ってくるので、われわれの意識はそのなかでももっとも 大きな、ということはもっとも注意をひく情報に向けられているということであろう。 電子計算 機の父といわれる故ノイマン博士の計算によれば、人間が一秒間に受けとる情報の量は一四〇〇ビットぐらいだといわれる。一ピッドというのは、イエスかノーかという情報単位であるが、 これは、われわれが知っているもっとも大きな電子計算機の記憶一〇〇万ビッドの十四万倍と いう大量のものである。これだけ大量の情報をいちいち意識することはとうてい不可能であり、 そこでわれわれの意識は、そのなかから注意を要する情報にだけ意識を向けているというわけで ある。だから、意識されなくても情報はつねに入っており、意識されない情報もあるということ になる。
そこでいままでのところをとりまとめると、こういうことになる。
1意識されない情報
2刺激経験知覚情報 2意識された情報
さて、つぎに、これらの情報が「記憶」になるわけだが、われわれは、たとえ知覚したり、感 じたりすることができても、これが記憶に残らなかったら、 「情報」として活用することはでき ない。つまり、ほんとうの情報にはなり得ないということである。 そこで問題になるのは、意識 された情報は論外として、意識されない情報はどうなのか、それも記憶になるものかということ である。しかし、これも考えてみると、スキーや水泳のように、いちいち意識しない動作でも、 練習による繰り返しを肉体がおぼえていて、これの積み重なりが熟練になるわけだから、つまり は、意識されない情報も、記憶のなかにくりこまれるということになる。そこでもっとも簡単な いい方をすれば、見たり、聞いたり、さらにそのほかのあらゆるかわ
によって感知され、これらを
新しい事態が発生すると、われわれの感覚器官は、その事によってひきされた
送り、脳はこれらの信号を感知することによって情報を得る。 これは、いうなれば「外部情報」 というべきだろう。
つぎに、脳は、以前から持っていた記憶を「内部情報」としてひきだし、外部情報と照らしあ わせることによって、はじめてこの事態を判断することになる。だから、もし、われわれが 生まれてからこのかた、ずっと感覚器官のはたらきが不完全であったら、われわれの脳のなかに ある記憶は非常に貧弱なものとなり、したがってわれわれの判断は正確を欠くことになる。だか ら、感覚器官の錬磨洗練ということは非常に大切なことであり、このことはあとになって関連す ることが出てくるから、よく記憶しておいてほしい。
さて、そこで、今までのところを総括すると、こういうことになる。
刺激(経験) 知覚情報
意識されない情報」 意識された情報
記憶
前世の記憶
では、記憶は脳のどこにたくわえられるのであろうか?
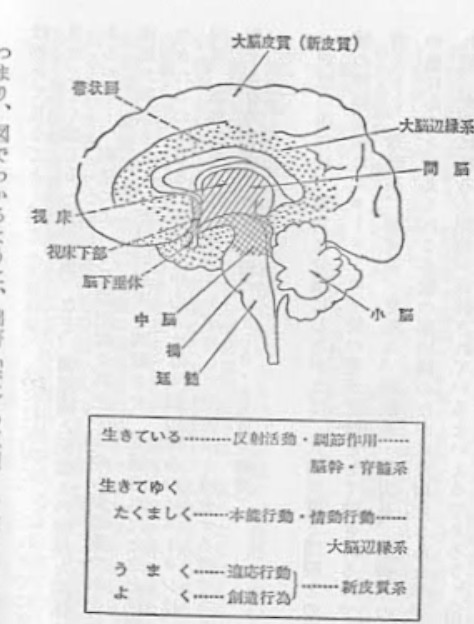
それは、大脳の側頭葉と、海馬を中心とした領域でなされるようである。
そこで、
実際に、海馬や側頭葉がこわされると、いろいろな型の記憶障害がおこることが、動物や人間 についてたしかめられている。また、側頭葉の電気刺激で過去の体験を再現することに成功した ペンフィールド博士の実験(旧)や、ネズミの海馬をこわすと判別能力がわるくなるという 条件行動の実験も、側頭葉や海馬が記憶やそれにもとづく判断のはたらきに直接関係しているこ とを示している。ただし、それは、側頭葉と海馬だけが記憶の貯蔵所という意味ではなく、記憶 はある程度、脳全体に分布しており、側頭葉と海馬は、その中心としてはたらく機能を持ってい る場所であるというように考えられている。
側頭葉は記憶の機能に密接な関連をもつ。記憶に、海馬を中心とした辺縁系が重要であること は前にものべたが、それを含む側頭葉切除では、古くたくわえられた記憶は失われないが、新し い情報を記憶に組みこみ、早期にそれを固定し、必要に応じてそれを引き出して用いるはたらき <記銘と回想)に重要な障害をきたすことが、脳外科的手術の経験の増すとともに確かめられた。 前頭葉の破壊によって古い記憶障害されにくいところをみると、記憶は広く全脳にたくわえら れるものであって、側頭葉はその出し入れと照合(解釈)に主役を演ずるものらしい』(脳のはた らき・島崎敏樹 宮坂松術著) そしてそれは海馬もおなじようなはたらきをするものと考えられる。 『記憶は多分、視床の連合や、大脳皮質では第二次運動野、第二次知覚野および連合野でたく わえられる。 触覚性の行動の 身体の部分に対応した 、
また、側頭葉表面の刺激で、短期記憶がさまたげられることや、見れているものが自覚的 初めて見るごとく感じ(未体験)、または反対に、これまでに見たことのないものが、以前に 見たごとく感じる(既視体験など、側頭葉と記憶との密接な関係はよく知られているところで あるが、刺激によって長期記憶を再生するのも側頭葉であるが、それは多分、側頭葉深部の 海馬が刺激されて、記憶貯蔵所を興奮させ、記憶されたときと同様な型の興奮を生じ、記憶が再 生されるのである。海馬を中心とする大脳辺縁系のニューロンは、知覚系、 運動系、覚醒系、動 制御系その他の機能系を連合して記憶と結合する道であり、記憶をたくわえ、または再 生する有力な道である』(脳のはたらき・吉井直三郎著)
記憶の所在は、粗大な分類にしたがえば、大脳皮質と間脳との間の広汎な領域にある。 その領 城の神経連鎖にニューロンの活動の型が記憶として残されるのであろうが、これを細胞レベルで 考えると、運動系、知覚系、覚醒系、睡眠系、動因系、制御系のいずれにあっても、その主回路 他にあると考えられる多数の副回路のなかに反射化された学習回路が残されるのであろう。 そ 故、大脳にひろく記憶が保持されているといえるであろう』(脳のはたらき 吉井直三郎著) 以上の専門学者の説明を参照した上で、私の求聞持法の体験をあわせ判断すると、記憶の場 半球内側面で間をかこむ部分、つまり「帯状回」のあたりであると私は思う。
be The brain will know what it is by its function. He says he "perceived" this. In other words, in the case of a red flower, the pulse that travels through the optic nerve and reaches the visual cortex in the occipital lobe of the brain first perceives the ``red flower''. When we say ``hear,'' there is an air vibration that is pulsed from the receptors in the eardrum and reaches the brain, where it is ``sounded'' by the area at the base of the temporal lobe called hearing. It means that we have the perception as What we know so far is that the pulse from the receptor has nothing to do with the type of receptor in the subsequent neurotransmission mechanism, and becomes purely a matter of the pulse. In other words, it depends only on how many pulses are emitted or not. It means that it can be done. Now then, this “perceived” thing becomes one piece of “information” for us.
Stimulus (experience) → Perception → Information
In other words, we've made it this far.
This is what happens.
However, there is one very important thing here.
That is, the perception may not be "conscious". He said that even if a receptor sends out a pulse that reaches and is perceived, it is not necessarily conscious. "I see, but I do not see, I hear, he said, but he does not. In other words, he perceives, but he is not conscious.
Then, do such unconscious signals not become information?
The word stimulus experience seems to have to be accompanied by consciousness. In other words, unconscious stimuli cannot become experiences. What do you think? However, if you think about it, he said that in our daily actions, when it is a common action, it is very rare for us to exercise our consciousness. In the case of familiar movements and tasks, most of them are done unconsciously. For example, when we perform a very common action such as ``walking down the street'', we are doing the action of walking almost unconsciously. If he was conscious of the information from the sensory organs on the back of his feet, he would not be able to do it. However, when an abnormal condition occurs, such as tripping over something, consciousness kicks in immediately. In other words, until then, we had been receiving information that there was no abnormality, but our consciousness did not pay attention to it, and the moment an abnormality occurred, we immediately turned our attention back to that. deaf.
What can be thought of here is that the information we receive is not always one at a time, but rather a large amount of information comes in at the same time. It is likely that it is aimed at attracting information. According to the calculations of the late Dr. Neumann, who is known as the father of electronic computers, the amount of information that humans receive per second is said to be about 1,400 bits. A pid is a unit of yes or no information, which he says is 140,000 times the memory of the largest electronic computer we know of, 1,000,000 bids. . He argues that it is impossible to be conscious of such a large amount of information one by one, and that our consciousness is focused only on the information that requires our attention. Therefore, even if we are not conscious of it, we always have information, and there is also information that we are not conscious of.
Summarizing what has been said so far, we have the following.
1 Unconscious information
2 stimulus experience perceptual information 2 conscious information
Now, next, this information becomes ``memory''. Can not. In other words, it cannot be real information. The question then becomes whether the conscious information is out of the question, and what about the unconscious information, and whether it becomes a memory. However, if you think about it, you will find that even if you are not consciously doing something like skiing or swimming, your body will remember the repetitions of practice, and the accumulation of these will make you skilled. It's going to be stuck in your memory. So, in his simplest terms, seeing, hearing, and all sorts of other
are sensed by
When a new event occurred, our sense organs were triggered by it.
The brain obtains information by sensing these signals. This should be called "external information".
Next, the brain draws out the memory it has had for a long time as "internal information" and compares it with external information to make a judgment about the situation. If, therefore, our sense organs have been imperfect all our lives, our memories of her in our brains will be very poor, and our judgments will therefore be inaccurate. will be lacking. Therefore, the training and refinement of the sense organs is very important, and I would like you to remember this well, as it will be related later.
So, to summarize what has happened so far, this is what happens.
Stimulus (experience) Perceptual information
Unconscious information Conscious information
Memory
memory of previous life
Where in the brain are memories stored?
It seems to be done in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum and the area centered on the hippocampus.
Therefore,
In fact, it has been confirmed in animals and humans that damage to the hippocampus and temporal lobes can lead to various types of memory impairment. In addition, Dr. Penfield's experiment (old), in which he succeeded in reproducing past experiences by electrical stimulation of the temporal lobe, and an experiment on conditioned behavior, in which the hippocampus of rats was damaged, their discriminative ability deteriorated, were also conducted in the temporal lobe. and the hippocampus are directly related to memory and judgment based on it. However, this does not mean that the temporal lobe and the hippocampus are the only storage areas for memory. Memories are distributed to some extent throughout the brain, and the temporal lobe and the hippocampus are places that function as the center of memory. It is thought that there is
The temporal lobe is closely related to memory functions. I mentioned earlier that the limbic system centered on the hippocampus is important for memory. Temporal lobectomy, which includes the hippocampus, does not lose old memories, but it does not lose new information. It was confirmed with increasing experience of neurosurgical operations that the function of incorporating it, fixing it at an early stage, and pulling it out and using it when necessary causes important obstacles to the function (memorization and recollection). Looking at the fact that old memories are less likely to be damaged by destruction of the frontal lobe, it seems that memories are widely stored throughout the entire brain, and that the temporal lobe plays a major role in the retrieval and collation (interpretation) of memories. Taraki, Toshiki Shimazaki, Matsujutsu Miyasaka) And it is thought that Kaiba also works in the same way. "Memories are probably stored in associations in the thalamus and, in the cerebral cortex, in the secondary motor, secondary sensory and association areas. corresponding to body parts of tactile behavior,
In addition, stimulation of the surface of the temporal lobe may interfere with short-term memory, subjective feeling that what is being seen is as if it is the first time (unexperienced), or, conversely, that something that has never been seen before may be subjective. (Although the close relationship between the temporal lobe and memory, such as déjà vu experience, is well known, it is also the temporal lobe that reproduces long-term memory by stimuli. The hippocampus in the deep part of the temporal lobe is stimulated, excites the memory storage, produces the same type of excitement as when memorized, and recalls the memory. Neurons are pathways that link sensory, motor, arousal, dynamic control, and other functional systems with memory, and are powerful pathways for storing and reproducing memories. by Naosaburo Yoshii)
Memory is located in a broad area between the cerebral cortex and diencephalon according to coarse classification. The type of neuron activity is probably left as memory in the neural chain of that territory. Even if there is, it will leave the learning circuit reflected in the many possible sub-circuits of the main circuit. Therefore, it can be said that the brain retains a wide range of memories.” Then, I think that it is around the cingulate gyrus, which is the area surrounding the medial hemisphere of the memory field.






















